Liver (Hepatic)
Liver Tumour Removal :
To remove a tumour, a surgical procedure is adopted called partial hepatectomy, wherein a part of the liver affected by the tumour is removed.
Liver resection is also used to remove cancers that have spread to the liver from other locations, including metastasized colorectal cancers and large-sized colorectal cancers. It is a major surgical procedure conducted by hepatobiliary surgeons.
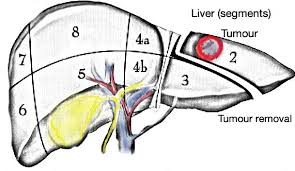
The body can cope with the removal of up to two-thirds of the liver. Post-surgery, the liver can grow back. Within 3 months of the surgery, the liver will have grown back to a near-normal size. Meet our specialist for liver tumour removal in Bangalore.
Deceased & Living Donor Liver transplantation
The surgical procedure that involves placing a liver graft either as a whole organ or a part is referred to as a liver transplant. Liver transplants have been categorised as
DDLT, deceased donor liver transplantation
This is also termed as Orthotopic transplant, which is the most commonly used procedure, wherein a whole liver is taken from a recently deceased donor and implanted in the patient. Meet our expert doctors for deceased donor liver transplantation in Bangalore.
LDLT, living donor liver transplantation:
There are three phases in the physiology of a transplant:
– Resection or ‘pre-anhepatic’ phase. Here liver dissection is carried out.
– Anhepatic phase. the period of time when no liver is in the circulation
– post-reperfusion phase). Also known as the Neohepatic phase, the stage at which the donor liver begins to function.
Hydatid Cyst:
The primary cause of hydatid cysts originates from tapeworms, a parasitic worm that lives in the guts of animals and humans. They enter the body in the form of larvae, and the eggs hatch into embryos that penetrate through the intestinal walls, get carried through the bloodstream to vital organs, and result in the formation of watery blisters. Identified as a hydatid cyst, with the liver being one of the potential organs to be affected. Hydatid disease is a probable fatal disease in the event of a lack of timely diagnosis and treatment. A heavily infested organ may fail or a cyst may rupture, resulting in a life-threatening allergic reaction.
The Symptoms of Hydatid Cyst are:
- Upset stomach.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Abdominal swelling.
- Weakness and fatigue.
- Severe cough.
- Blood or the fluidic discharge while coughing.
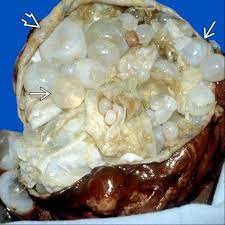
The treatment for hydatid cysts is primarily a surgical procedure that is supplemented with anthelminthic medication to eliminate any leftover tapeworm eggs.
Large Haemangioma:
A liver hematoma is a noncancerous mass in the liver made up of a tangle of blood vessels. It is also known as hepatic hematoma or cavernous hematoma.
These tumours are mainly asymptomatic and do not require treatment. However, certain special cases call for surgical intervention as the line of treatment.
Various diagnostic Tests used to diagnose liver hematomas are:
- Ultrasound, an imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the liver
- Computerised Tomography (CT) scanning, which combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the liver
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technique that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the liver.
- Scintigraphy is a type of nuclear imaging that uses a radioactive tracer material to produce images of the liver.
Liver Trauma:
Most liver injuries occur from blunt trauma from road accidents, falls, bicycle crashes, violence, sports injuries that cause a blunt, forceful impact, or a penetrating injury that tears or cuts the liver.
Shunt Surgery for Portal Hypertension:
Portacaval shunting is a surgical treatment to create new connections between two blood vessels in your abdomen. It is used to treat people who have severe liver problems. The portal vein drains blood from the intestine, stomach, spleen, pancreas, and gallbladder into the liver.
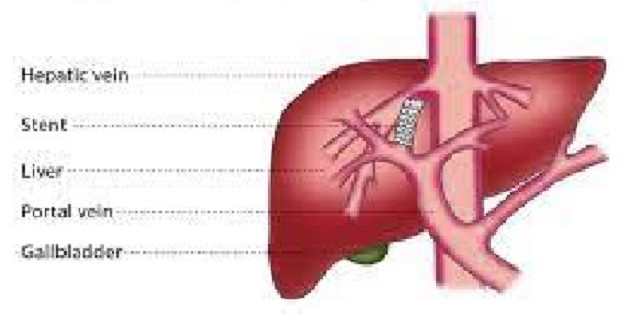
The primary objective is to reduce the pressure in the portal vein, thus maintaining regular blood flow around the liver, and to reduce the probability of hepatic encephalopathy, a condition causing cognitive, psychiatric, and motor impairments in the brain, resulting in
forgetfulness, confusion, and breath with a sweet or musty odour.
Advanced symptoms include shaking of the hands or arms, disorientation, and slurred speech.